VRayScatterVolume
Overview
The VRayScatterVolume material is designed solely as a brute force option for SSS to produce an unbiased result. When used as a base material in a VRayBlendMtl it can create complex materials with a subsurface scattering base.
UI Path
||Material Editor window|| > Material/Map Browser > Materials > V-Ray > VRayScatterVolume
Properties
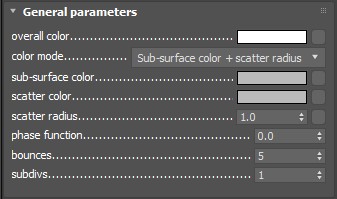
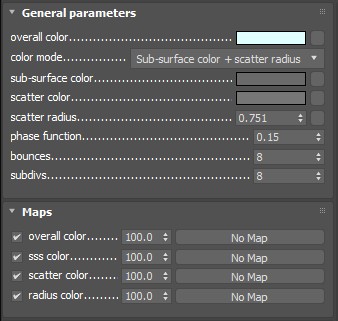
overall color – Controls the surface coloration for the material.
color mode – Allows the user to determine which method is used to control the sub surface scattering effect.
Sub-surface color + scatter radius – The subsurface effect is controlled with the help of the sub-surface sss color and scatter color parameters.
Scatter coefficient + fog color – The subsurface effect is controlled with the help of the scatter coefficient and fog colorparameters.
sss color – Specifies the general color for the sub-surface portion of the material.
scatter color – Specifies the internal scattering color for the material. Brighter colors cause the material to scatter more light and to appear more translucent; darker colors cause the material to look more diffuse-like.
scatter coefficient – Specifies the subsurface color, just beneath the surface of the material.
fog color – Specifies the deep inside color of the object.
scatter radius – Controls the amount of light scattering in the material. Smaller values cause the material to scatter less light and to appear more diffuse-like; higher values make the material more translucent. Note that this value is specified always in centimeters (cm); the material will automatically convert it into scene units based on the currently selected system units.
phase function – A value between -1.0 and 1.0 that determines the general way light scatters inside the material. Its effect can be somewhat likened to the difference between diffuse and glossy reflections from a surface, however the phase function controls the reflection and transmittance of a volume. A value of 0.0 means that light scatters uniformly in all directions (isotropic scattering); positive values mean that light scatters predominantly forward in the same direction as it comes from; negative values mean that light scatters mostly backward. Most water-based materials (e.g. skin, milk) exhibit strong forward scattering, while hard materials like marble exhibit backward scattering. This parameter affects most strongly the single scattering component of the material. Positive values reduce the visible effect of single scattering component, while negative values make the single scattering component generally more prominent. For more information, see the Phase Function example below.
bounces – Controls the number of bounces a ray of light makes inside the volume.
subdivs – Controls the quality of the sub-surface scattering. Lower values produce a faster but noisier result. Higher values reduce the noise but increase the render times. Note that this parameter is available for changing only when Use local subvis is enabled in the Global DMC Settings.
Example: Phase Function
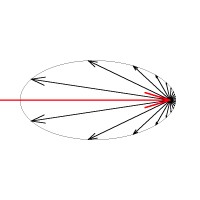
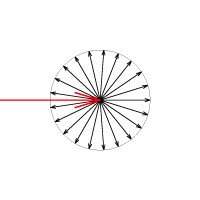
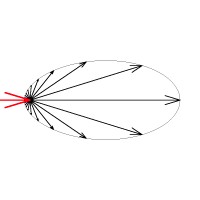
These images represent the how different values of the phase function parameter affect the raytracing inside the volume. The red arrow represents a ray of light going through the volume; the black arrows represent possible scattering directions for the ray.
phase function = -0.5 (Backward Scattering)
phase function = 0 (Isotropic Scattering)
phase function = 0.5 (Forward Scattering)
Advanced Parameters
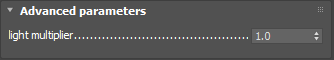
light multiplier – Controls the effect that direct light has on the material. This multiplier does not affect GI that the material receives. Very scattering materials like snow may require a large number of light bounces (>200) to look plausible, and this may be impractical. The light multiplier parameter can help brighten up such materials while using fewer light bounces. This is not physically accurate, but it could be a useful way to speed up renders.
Usage Notes
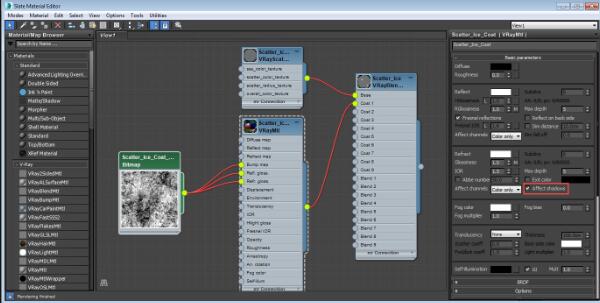
Normally, VRayScatterVolume would be a base material of a VRayBlendMtl material and the coat material will be a transparent or refractive VRayMtl material. You will get best results if the coat VRayMtl material has its Affect Shadows option enabled so that it lets light through more easily:
Sample Usage
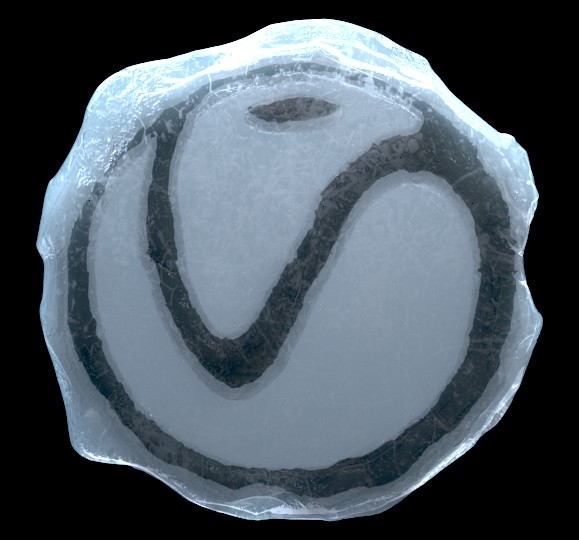
The ice chunk shown below was created as a dense mesh with a rough surface. Strong lights were placed to point at the object, both above and below it.

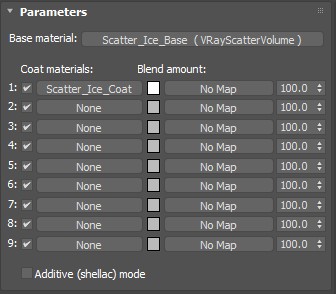
A single VRayBlendMtl was applied to the entire object. This material setup consists of the following:
-
VRayBlendMtl:
-
Base Coat: VRayScatterVolume
-
Coat 1: VRayMtl named Scatter_Ice_Coat
-
Blend amount: Pure white ( 255,255,255 ) , see Notes below
VRayScatterVolume Details
Note that the phase function value is a small positive number to create slight forward scattering.
VRayMtl Details
The VRayMtl creates the icy "coat" around the object. Settings include:
-
Reflection, Refraction, Fog colors: White
-
Bump, Reflection Glossiness, and Refraction Glossiness maps: Color Correction maps that adjust brightness and contrast of an ice bitmap. See Material Editor diagram above for a look at the bitmap.
Notes
-
When using VRayBlendMtl with VRayScatterVolume as base and a refractive VRayMtl as coat, it is strongly recommended to assign pure white as the blend amount, otherwise the result will not be physically accurate and it will lead to longer render times

